In construction projects, aluminum magnesium manganese plate, as an excellent metal material, has become one of the preferred materials for roofs and exterior walls due to its lightweight, high strength, corrosion resistance, and ease of processing. However, many project managers are confused when choosing aluminum magnesium manganese sheets of different thicknesses and models. This article will provide a detailed analysis of the key factors in choosing the thickness of aluminum magnesium manganese plates, helping you make the most appropriate decision.
1. Understand the basic characteristics of aluminum magnesium manganese plates
Aluminum magnesium manganese plate is a metal sheet made of aluminum as the basis and added with alloy elements such as magnesium and manganese. It has the advantages of lightweight, high strength, corrosion resistance, and strong plasticity.
These characteristics make it a widely used material in modern architecture, from large public buildings to industrial plants, and even residential buildings.
The market share of aluminum magnesium manganese alloy plates in the construction industry has exceeded 55%, which fully demonstrates its important position in the industry.
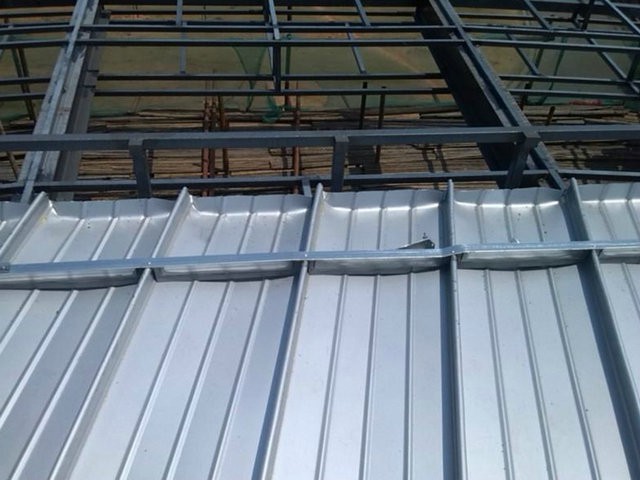

2. Common thickness range of aluminum magnesium manganese plate
The thickness of aluminum magnesium manganese plate is generally between 0.7mm and 1.2mm, and the specific products of different manufacturers may vary slightly.
The conventional thicknesses include 0.7mm, 0.8mm, 0.9mm, 1.0mm, and 1.2mm.
This thickness range has been verified through long-term practice, which can ensure performance while balancing economy and construction convenience.
Thinner aluminum magnesium manganese plates (such as 0.7mm, 0.8mm) are suitable for lightweight buildings or projects with strict weight restrictions. They can provide sufficient strength and stability while reducing building loads.
Thicker aluminum magnesium manganese plates (such as 1.0mm, 1.2mm) can provide higher strength and stability, suitable for large industrial plants, sports venues and other buildings, meeting higher load requirements.
3. Five key factors determining board thickness
1. Building type and purpose
The thickness requirements for aluminum magnesium manganese plates vary greatly among different types of buildings.
Large public buildings (such as airports, sports venues, stations, etc.) typically require thicker panels ranging from 0.9mm to 1.5mm, as these buildings often have large spans and higher requirements for roof load-bearing capacity and wind pressure resistance.
Small civil buildings (such as villas and residential communities) can use thinner panels ranging from 0.7mm to 1.0mm, which have relatively simple structures and lower load requirements.
2. Environmental load conditions
The wind load and snow load of the building environment are key factors determining the thickness of the slab.
Strong wind areas: Coastal areas or open areas with strong winds should choose thicker boards to enhance wind resistance.
Snowy areas: Areas with thick snow require thicker sheets to withstand snow loads and prevent roof deformation.
Aluminum magnesium manganese plates require high strength and stiffness to withstand large wind and snow loads.
3. Support spacing and span
The spacing between purlins is a direct factor determining the thickness of the slab.
Large span: When the spacing between purlins is large (usually exceeding 1.5 meters), thicker plates should be selected to ensure the rigidity of the plate surface and prevent deformation.
Small span: When the spacing between purlins is small, relatively thin boards can be selected to meet the stiffness requirements.
4. Durability requirements
The design service life of a building is directly related to the selection of material thickness.
Long term use: For buildings that require a long service life (such as over 25 years), thicker panels should be selected to ensure that their performance is not affected by corrosion or deformation during their service life.
Short term use: For temporary buildings or buildings with low service life requirements, thinner panels can be chosen to save costs.
Aluminum magnesium manganese plate, due to its strong corrosion resistance and the naturally formed dense alumina protective film on the surface, can maintain good performance for a long time even in harsh environments.

5. Economic considerations
Under the premise of meeting technical requirements, economy is an undeniable factor.
Initial investment: Thicker boards have higher prices and will increase initial investment.
Long term benefits: Thicker sheets typically have a longer service life and lower maintenance costs, and may be more economical from a full lifecycle perspective.
4. Matching selection of thickness and model
There are two main systems for aluminum magnesium manganese plates: upright double locking edge (high standing edge) and upright single locking edge (low standing edge).
1.65 series (high standing edge): The standing edge height is 65mm, and the commonly used thickness is 0.9mm-1.5mm. This system is suitable for large public buildings and harsh weather environments because it has better load capacity and wind resistance performance.
2.25 series (short standing edge): The standing edge height is 25mm, and the commonly used thickness is 0.7mm-1.0mm. This series is usually used for buildings with high aesthetic requirements such as villas and concrete foundation roofs.
When choosing, not only should thickness be considered, but also plate type, because the structural performance of different plate types is different, and even if the thickness is the same, their bearing capacity will vary.
5. Thickness adjustment for special environments
In certain special environments, special consideration needs to be given to the thickness selection of aluminum magnesium manganese plates:
1. Coastal areas: Salt spray corrosion is severe, and thicker plates should be selected. Consider using 3004/3105 series aluminum magnesium manganese plates with specific alloy formulas, which can effectively resist salt spray erosion.
2. Industrial pollution zone: The air contains corrosive substances, and the plate thickness should be appropriately increased to extend its service life.
3. High cold regions: large temperature differences and significant thermal expansion and contraction effects, thicker sheets should be selected to reduce the risk of deformation. Some manufacturers have also specifically developed aluminum magnesium manganese roof panels suitable for cold regions, which perform well in low-temperature toughness and thermal insulation.
6. Thickness recommendations for common application scenarios
Based on years of practical experience, the following are some recommended thicknesses for aluminum magnesium manganese plates in common application scenarios:
1. Large transportation hubs such as airports and stations: It is recommended to use 65 series high standing edge panels with a thickness of 1.0mm or more, as these places have high pedestrian flow, high safety requirements, and often high building acoustic requirements.
2. Sports venues and exhibition centers: It is recommended to use 65 series high standing edge panels with a span of 0.9mm-1.2mm. These types of buildings have large spans and may have complex shapes, requiring good load-bearing capacity and formability.
3. Commercial and industrial buildings: It is recommended to use 0.8mm-1.0mm aluminum magnesium manganese sheets, adjusted according to specific span and load requirements.
4. Villas and residential communities: It is recommended to use 25 series low standing edge panels with a thickness of 0.7mm-0.9mm. These types of buildings place more emphasis on aesthetics and cost control.
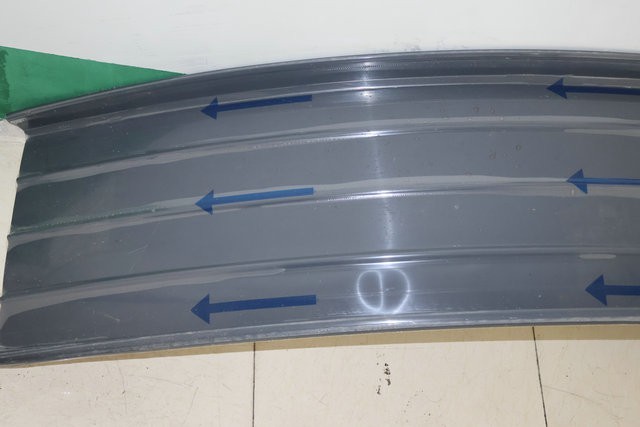

7. Improper selection of potential risks
Choosing the wrong thickness of aluminum magnesium manganese sheet can cause a series of problems:
1. Risk of insufficient board thickness:
Insufficient bearing capacity, prone to deformation under wind and snow loads.
Shorten the service life, repair or replace in advance.
Weak wind resistance and potential safety hazards.
Discounted sound insulation and thermal insulation effects.
2. The problem of excessive board thickness:
Unnecessary increase in material costs.
The construction difficulty has increased and the processing is inconvenient.
To increase the load on the building structure, it is necessary to strengthen the support.
Material waste violates the principles of green building.
8. Suggestions for the Professional Selection Process
To ensure the selection of the most suitable thickness for aluminum magnesium manganese plates, it is recommended to follow the following process:
1. Clarify building requirements: Determine the building type, functional use, and design service life.
2. Analyze environmental conditions: Investigate the climatic conditions of the building location, including wind loads, snow loads, and corrosive substances.
3. Determine structural parameters: Understand the support spacing and span of the roof or wall.
4. Load calculation requirements: Calculate the required bearing capacity based on the above information.
5. Preliminary selection of plate thickness range: Determine the plate thickness range based on the calculation results.
6. Consider economic factors: Adjust the thickness selection according to the budget while meeting technical requirements.
7. Consulting professionals: Consult with relevant professionals such as building engineers, architects, or professional contractors to obtain professional advice.
8. Final specification determination: After considering all factors comprehensively, determine the final plate thickness and shape.
9. Future Development Trends of Aluminum Magnesium Manganese Plate
With the promotion of green building concepts, there is an increasing demand for the performance and environmental protection of building materials.
Aluminum magnesium manganese plate, due to its environmentally friendly and sustainable characteristics, is in line with the current development trend of the construction industry.
In the future, the development of aluminum magnesium manganese plates will focus on high-performance, green, and expanded application scenarios.
With the deepening promotion of green building concepts, the demand for energy-saving, environmentally friendly, and recyclable metal materials continues to grow. Aluminum magnesium manganese plate, as an important representative of low-carbon building materials, is expected to be widely used in emerging building systems such as prefabricated buildings and passive houses.
Choosing the appropriate thickness of aluminum magnesium manganese plate requires finding a balance between technical requirements and economy. Thicker boards (1.0mm-1.2mm) provide higher strength and stability, suitable for large industrial plants, sports venues and other buildings; Thinner sheets (0.7mm-0.8mm) are suitable for lightweight buildings or projects with strict weight restrictions.
Please make the final decision based on the advice of professional designers and make comprehensive considerations according to the actual project needs. Only by selecting the appropriate thickness of aluminum magnesium manganese plates can the safety, durability, and economy of buildings be ensured.
 Language
▼
Language
▼


