 Language
▼
Language
▼
More Language
In modern construction, home appliances, transportation, and decoration industries, color-coated steel sheets have become one of the most representative surface-treated metal products due to their excellent corrosion resistance, rich color expression, and good processing performance. Combining the mechanical strength of steel sheets with the decorative and protective properties of organic coatings, color-coated steel sheets are widely used in roofing, wall cladding, doors and windows, appliance housings, transportation equipment, and other fields.
Color-coated sheets typically use galvanized steel sheets, aluminum-zinc alloy sheets, or cold-rolled steel sheets as substrates. A robust protective film is formed through multi-layer coating and high-temperature baking/curing. The entire production process employs a continuous coating production line, with equipment typically comprising uncoilers, cleaning units, chemical treatment units, coating units, baking ovens, cooling devices, and rewinders. Each step in the production flow is interconnected, from raw material pretreatment to finished product packaging. Every stage directly influences the surface quality, adhesion, durability, and final appearance of the color-coated sheet.

Surface treatment is the first critical process in color-coated sheet production. Its purpose is to remove scale, rust, oil, and impurities from the metal substrate surface, providing a clean, active substrate for subsequent coating adhesion.
Surface treatment generally employs two methods:
- Mechanical methods: Physically removing surface oxides and impurities through sanding, polishing, or sandblasting, suitable for heavily rusted or rough steel sheets;
- Chemical methods: Cleaning oils, oxide films, and contaminants using acid washing, alkali washing, or surfactant solutions, followed by thorough rinsing with water.
In most modern production lines, chemical methods are more prevalent, typically employing multi-stage acid/alkali cleaning processes. After cleaning, the sheet surface must proceed to the next process promptly to prevent re-oxidation and rusting. Additionally, following surface cleaning, chemical conversion treatment is required. This forms a dense conversion coating on the metal surface to enhance coating adhesion and corrosion resistance.
The primer serves as the foundational layer of the color-coated sheet coating system, providing corrosion resistance, enhancing adhesion, and improving overall durability. Primer selection depends on substrate type and usage environment. Common primers include epoxy, polyester, and polyurethane types, all requiring excellent chemical resistance and adhesion. Prior to application, primers must be thoroughly stirred and filtered to remove impurities and air bubbles, ensuring coating uniformity. Coating application can be performed using roller coating to ensure consistent coating thickness and uniform coverage.
During application, the following key points must be controlled:
- Match coating viscosity with application speed to prevent sagging, pinholes, or missed areas;
- Ensure primer thickness is generally around 5-7μm;
- The coating should fully adhere to the sheet surface, avoiding bubbles or poor adhesion.
After primer application, sheets enter a curing oven for solidification.
Curing is critical for coating solidification, determining paint film adhesion, hardness, and durability. Primer curing typically employs a high-temperature hot-air oven at approximately 100°C for 10-15 minutes. During drying, insufficient temperature may result in incomplete curing and reduced adhesion, while excessive heat can cause paint film brittleness or color distortion. Therefore, precise temperature control and uniform airflow distribution within the oven are essential to ensure consistent heating across the entire coil. After drying, the sheet passes through a cooling section to bring its surface temperature down to ambient levels before proceeding to the next process.
The topcoat is the core component determining the appearance and performance of color-coated steel sheets. It directly influences the product's color, gloss, weather resistance, and decorative effect. Beyond aesthetics, the topcoat must possess comprehensive properties including UV resistance, oxidation resistance, high-temperature resistance, and corrosion resistance.
Common topcoat types include:
- Polyester (PE): Vivid colors, moderate cost, suitable for general construction applications;
- Silicone-modified polyester (SMP): Superior weather resistance compared to PE, suitable for outdoor applications;
- Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF): Exceptional UV resistance and corrosion resistance, commonly used in high-end construction;
- High-Durability Polyester (HDP): Balances cost and performance, widely popular in the market.
Topcoat application also employs roller coating, with higher operational requirements than primer application. It demands uniform coverage and precise thickness control. Typically, topcoat thickness ranges between 15-25μm.
The temperature and duration for topcoat curing must be adjusted according to the paint type and thickness. Typically, the temperature is maintained around 120°C for approximately 15-20 minutes. High-temperature curing fully cross-links the resin in the paint film, forming a dense protective layer that imparts excellent corrosion resistance and gloss stability to the color-coated sheet. The dried surface should be smooth, free of bubbles and pinholes, with consistent color. After drying, the sheets pass through a cooling unit to prepare for subsequent quality inspection and coiling.
Quality inspection is a critical step before coating sheets leave the factory, ensuring each roll meets standard requirements. Key inspection items include:
- Visual inspection: Check surface flatness, color uniformity, and absence of defects like pinholes, sagging, or cratering;
- Thickness measurement: Use a coating thickness gauge to verify primer and topcoat thicknesses meet process specifications;
- Adhesion testing: Evaluate coating adhesion via cross-hatch or peel tests;
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: Includes salt spray tests and humidity tests to evaluate coating weatherability;
- Color Difference Inspection: Ensures color consistency across batches and meets customer specifications.
After passing inspection, color-coated steel sheets undergo protective film lamination, packaging, and coding before being stored or shipped to customers. Any anomalies detected trigger traceability to production stages for adjustments and improvements.
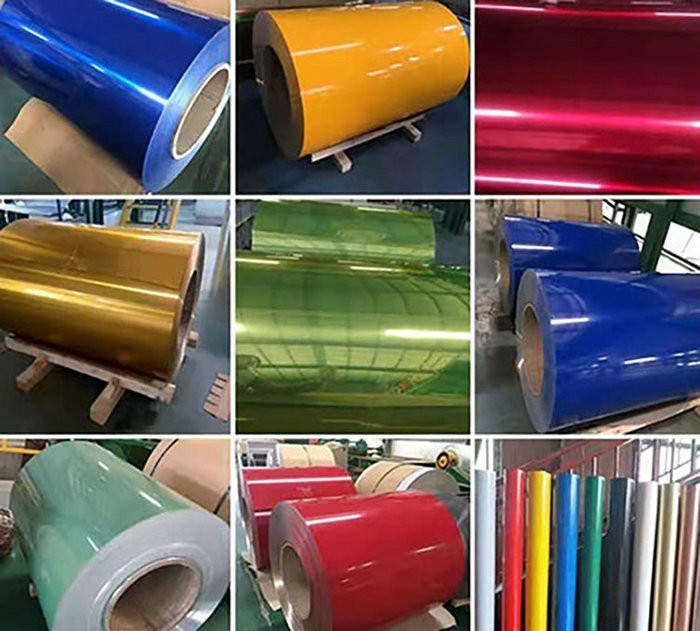

(1) Color-coated sheets offer exceptional decorative appeal. Their surfaces can exhibit diverse colors and gloss effects through varied coating formulations and application techniques. Whether vibrant hues or soft, subdued tones, they meet the aesthetic demands of diverse architectural styles, home decor, and industrial product designs. Furthermore, the coating's high surface flatness and refined texture enhance the sheets' visual elegance, significantly elevating the overall product appearance.
(2) Color-coated sheets demonstrate exceptional corrosion resistance. While bare metal sheets are prone to oxidation and damage from acids, alkalis, and other chemicals in natural environments, the organic coating acts as a robust protective barrier. This coating effectively isolates the metal substrate from air, moisture, and corrosive agents, significantly extending the sheet's service life. In harsh environments like coastal areas or chemical plants, color-coated steel sheets demonstrate a more pronounced corrosion resistance advantage over ordinary steel sheets. They maintain excellent condition over extended periods, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
(3) Color-coated sheets offer excellent workability. Inheriting the superior formability of metal sheets, they can be processed through various techniques—including cutting, bending, and stamping—to produce components of diverse shapes and specifications. During fabrication, the coating remains intact and retains its properties without peeling or damage due to sheet deformation. This makes color-coated steel sheets highly advantageous for manufacturing parts in industries like construction, automotive, and home appliances, meeting diverse production demands.
(4) Color-coated sheets also exhibit good weather resistance. They maintain stable performance in both high-temperature, hot regions and cold, low-temperature environments. The coating does not crack or peel due to temperature changes, withstanding prolonged sun exposure, wind and rain erosion, and alternating temperature and humidity cycles. This ensures reliable product performance under varying climatic conditions.
(5) Color-coated sheets also demonstrate fire-resistant properties. Some sheets coated with specialized fire-retardant coatings exhibit excellent flame-retardant characteristics. In the event of a fire, they effectively slow the spread of flames, buying valuable time for evacuation and firefighting operations. This enhances the fire safety standards of buildings and equipment.
(6) Color-coated sheets possess self-cleaning properties. The coating surface of certain sheets features unique microstructures and chemical characteristics that resist dust and stain adhesion. Even minor surface grime can be naturally washed away by rain, maintaining a clean and aesthetically pleasing appearance while reducing maintenance efforts.
(7) From an environmental perspective, color-coated sheets offer multiple advantages. On one hand, advanced coating technologies used in production minimize volatile organic compound emissions, reducing environmental pollution. On the other hand, these sheets are recyclable. At the end of their service life, specialized recycling processes separate the metal substrate from the coating. The metal can then be remelted and reprocessed, enabling resource circulation and aligning with sustainable development principles.
Color-coated steel sheets have extensive applications across multiple industries including construction, home appliances, and transportation. Below are several typical application scenarios:
Color-coated steel sheets are commonly used for building exteriors, roofs, and partition walls, offering both aesthetic appeal and functional benefits such as waterproofing and thermal insulation. They are particularly prevalent in commercial buildings, factories, warehouses, and similar projects.
Some appliance casings, such as those for refrigerators and washing machines, are made from color-coated steel sheets. This enhances product aesthetics while improving durability.
The exteriors of transport equipment like rail cars and shipping containers sometimes utilize color-coated sheets to reduce weight and enhance corrosion resistance.
Color-coated sheets are also employed in interior wall and ceiling decoration projects. Their diverse colors and textures add personalized elements to spaces.
The production of color-coated sheets is a systematic process integrating chemical treatment, mechanical processing, and automated control. Each step—from surface preparation to coating, drying, and inspection—requires strict adherence to technical parameters and operational standards. High-quality color-coated sheets depend not only on raw material selection but also on refined production processes and meticulous management. With continuous upgrades in equipment technology and heightened environmental standards, future production will evolve toward greater efficiency, energy savings, sustainability, and intelligence. This advancement will deliver higher-performance, more aesthetically pleasing, and eco-friendly metal material solutions for industries including construction, home appliances, transportation, and decoration.
China galvanized plate manufacturer: Boxing Shuangshengda Steel specializes in galvanized sheet, galvanized steel plate,Colour steel plate etc.We have a full range of product specifications and types, low prices, and more than 20 years of experience, worthy of your trust