On a construction site,a galvanized plate component has been exposed to wind and rain for five years and still remains intact,while ordinary steel components have rusted in less than a year under the same conditions.
1.Get to know the two major members of the steel world
Steel,as the backbone of modern industry,has various types and properties.In the steel family,galvanized plate and ordinary steel are like a pair of brothers with distinct personalities,each playing different roles.Understanding the differences between them is crucial for selecting materials correctly and ensuring project quality.
The fundamental difference between these two materials lies not in their matrix composition,but in the thin layer of zinc coating-not only the surface difference,but also the essential leap in protective performance.Whether it is building structures,automobile manufacturing,or daily household appliance production,material selection is directly related to the product's lifespan and safety.

2.What is ordinary steel?The essential characteristics of basic materials
Ordinary steel,as the name suggests,refers to the most basic form of steel,mainly composed of iron and carbon,and containing small amounts of other elements.It is one of the most fundamental and widely used metal materials in industrialized societies.
From a chemical composition perspective,the carbon content in ordinary steel is usually between 0.05%and 1.5%,which determines the hardness and strength of the steel.In addition,ordinary steel may also contain elements such as manganese,phosphorus,sulfur,etc.The content of these elements varies,forming different grades and uses of ordinary steel.
The biggest advantage of ordinary steel is its low cost,simple production process,and good processing performance.It can be easily welded,forged,rolled,and machined to meet the needs of various shapes and applications.However,ordinary steel has a fatal weakness-its susceptibility to corrosion.When exposed to air,especially in humid or corrosive environments,ordinary steel will rapidly oxidize,forming the well-known rust.
3.What is galvanized plate?The evolution of steel with upgraded protection
Galvanized steel can be understood as an upgraded version of ordinary steel,which is a steel material coated with a layer of zinc on the surface of ordinary steel.This layer of zinc serves as a protective layer,effectively isolating the steel from contact with the external environment,thereby greatly enhancing its corrosion resistance.
The galvanizing process can be achieved through various methods,the most common of which are hot-dip galvanizing and electroplating galvanizing.Hot dip galvanizing is the process of immersing steel in molten zinc to form a thick zinc coating;Electrogalvanizing,on the other hand,forms a thin but uniform layer of zinc on the surface of steel through an electrolytic process.Both methods have their own advantages and are suitable for different application scenarios.
Galvanized steel not only retains the mechanical properties and processing characteristics of ordinary steel,but also obtains additional protection provided by zinc.This combination allows galvanized plate to have a much longer service life than ordinary steel while maintaining a relatively reasonable cost.
4.Core difference:Comprehensive multidimensional comparison
1.Anti corrosion mechanism and service life
The corrosion of ordinary steel is an electrochemical process.When steel is exposed to humid air,countless tiny primary cells form on the surface,and iron serves as an anode that is continuously oxidized,forming loose red rust(Fe?O3).Once this process begins,it will continue until the steel is completely corroded.
The protection mechanism of galvanized plate is more sophisticated,as it protects the base steel in two ways:firstly,the zinc layer acts as a physical barrier,isolating the steel from contact with corrosive environments;Secondly,as a sacrificial anode,zinc will preferentially corrode iron even if the coating is damaged,thus protecting the steel itself.This unique protective mechanism enables galvanized plate to maintain its corrosion resistance even in the event of scratches.
In practical applications,the service life of galvanized plate can reach 5 to 10 times that of ordinary steel,depending on environmental conditions and usage.In general atmospheric environments,galvanized plate can be used for over 50 years without requiring significant maintenance.
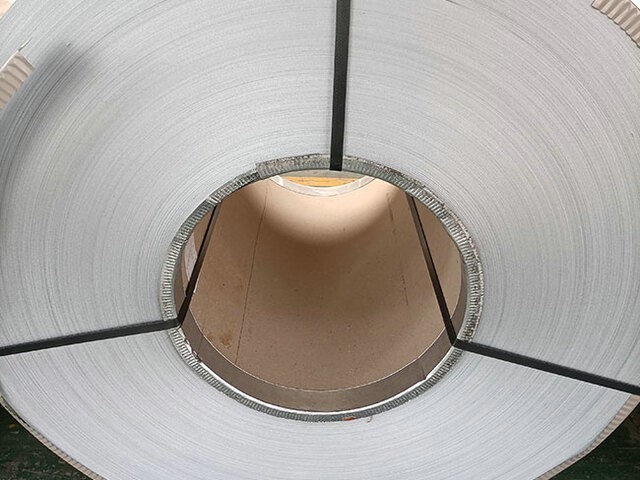


2.Physical characteristics and mechanical properties
In terms of physical properties,the two types of steel also exhibit significant differences:
Surface characteristics:The surface of ordinary steel is dark gray,with a relatively uniform texture;The surface of galvanized plate presents a bright silver color unique to zinc and has a typical zinc flower pattern.The presence of galvanized layer makes the surface of steel smoother and changes the friction coefficient.
Weight:Due to the lower density of zinc compared to iron,galvanized plate is slightly lighter than ordinary steel of the same specification,but the difference is not significant.
Welding performance:Ordinary steel has excellent welding performance and can be welded using various methods;The welding of galvanized plate is relatively complex and requires special techniques and parameters,as the melting point of zinc is low and zinc vapor is generated during the welding process.
Strength and hardness:The thermal effects during galvanizing,especially hot-dip galvanizing,may alter the mechanical properties of steel.Usually,the strength of galvanized plate slightly decreases,but ductility may be improved.
3.Cost benefit and economic analysis
From a direct cost perspective,the price of galvanized plate is usually 20%to 50%higher than ordinary steel of the same specifications,depending on the galvanizing method and zinc layer thickness.This price difference mainly comes from the equipment,energy,and material costs of the galvanizing process.
However,from the perspective of full lifecycle cost analysis,galvanized plate is often more economical.Regular rust prevention treatment,spray protection,and early replacement are required for ordinary steel,and these maintenance costs can accumulate into considerable amounts over long-term use.Galvanized steel significantly reduces maintenance requirements and frequency,resulting in lower overall costs in long-term projects.
For short-term projects or indoor applications,ordinary steel may still be an economical choice;But for structures that are used for a long time or in harsh environments,galvanized plate is undoubtedly a wiser investment.
4.Differences in Processing and Manufacturing
There are significant differences between the two types of steel during the processing:
Cutting and stamping:Ordinary steel does not encounter any special problems during these processing steps;When processing galvanized plate,the characteristics of the zinc layer need to be considered to avoid peeling or damage to the zinc layer.
Bending performance:Galvanized steel,especially hot-dip galvanized products,may experience microcracks in the zinc layer during bending,which usually does not affect corrosion resistance,but special attention should be paid in harsh environments.
Coating adaptability:Ordinary steel requires thorough surface treatment before coating;Galvanized steel surfaces are not easily adhered to conventional coatings and require specialized primers or special treatments.
5.Application areas:respective strengths in the stage
Based on the differences in the above characteristics,the two types of steel naturally form a division of labor in the application field:

1.Ordinary steel is mainly used for:
Short term construction projects and temporary structures
Application in indoor and dry environments
Substrate to be further processed or coated
Projects that are extremely cost sensitive and have high maintenance accessibility
2.Galvanized steel dominates the following fields:
Outdoor building structure and fence system
Body panels and structural components in the automotive industry
High altitude structures such as transmission towers and communication towers
Agricultural buildings and coastal facilities
Ducts and components in HVAC systems
3.Environmental adaptability and sustainability
Under different environmental conditions,there are significant differences in the performance of the two types of steel:
In the rural atmosphere,galvanized plate has the most prominent lifespan advantage and extremely low corrosion rate;In industrial environments,acidic pollutants accelerate the corrosion of two materials,but galvanized plate still maintains a significant advantage;In marine environments,high chloride ion content poses a severe challenge to both materials,but the zinc layer of galvanized plate can provide more effective protection.
From an environmental perspective,galvanized plate has significant sustainability advantages.Zinc itself is a completely recyclable material,and galvanized plate can be recycled as a whole after the end of its lifecycle.The long lifespan characteristic also means more optimized resource consumption and reduced waste generation.
6.Selection Guide:How to Make the Right Decision
When faced with material selection,the following key factors should be considered:
1.Environmental conditions:Evaluate the presence of corrosive substances,humidity,temperature fluctuations,and other factors
2.Expected lifespan:Determine the service life of a project or product design
3.Maintenance plan:Consider the accessibility and frequency of maintenance
4.Initial budget and lifecycle cost:Balancing short-term investment and long-term benefits
5.Aesthetic requirements:Evaluate the importance of appearance and surface characteristics
6.Processing requirements:Confirm the material requirements for subsequent manufacturing processes
Generally speaking,galvanized plate is a better choice in corrosive environments,difficult to maintain environments,and long-term use projects;In dry indoor environments,short-term use,or extremely cost sensitive situations,ordinary steel may be more suitable.
The choice between galvanized plate and ordinary steel is essentially a trade-off between initial cost and long-term value.Galvanized steel achieves a qualitative leap in anti-corrosion performance through the addition of a layer of zinc,providing reliable guarantees for long-term projects and structures used in harsh environments.Ordinary steel continues to play an irreplaceable role in suitable environments due to its economy and versatility.
Understanding the essential differences between these two materials not only helps to make technically sound decisions,but also optimizes project costs from a full lifecycle perspective.Today,with the continuous advancement of materials science,the galvanizing process is also constantly improving,providing more excellent anti-corrosion solutions for various industries.No matter which material is chosen,rational analysis based on actual needs is the fundamental aspect of engineering decision-making.
 Language
▼
Language
▼



